| Description: |
Floating point arithmetic can be achieved by moving the fractions into the integer. I.e. A floating point equitation using values with 3 digits after the dot can be calculated as follows:
Floating Point: 12.055 + 1.001 = 13.056
Integer: 12055 + 1001 = 13056 |
| Script: |
1.
2.
|
set /a y=12055 + 1001
echo.y = %y%
|
|
| Script Output: |
 Script Output Script Output | y = 13056
| |
| Description: |
The SET /A command can be used for basic arithmetic.
You can write SET /a y=3*x or SET /a y=3*%x%. Both are correct.
The command interpreter is smart enough to recognize variables within a formula. |
| Script: |
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
|
set /a x=20
set /a y=3*x
set /a y+=140
set /a y/=2
echo.y = %y%
|
|
| Script Output: |
 Script Output Script Output | y = 100
| |
| Description: |
An easy way to convert an ANSI encoded file to UNICODE is by running a TYPE
command in a new instance of CMD.exe with option /U and piping the output into a new file.
The following command converts a text file named myfile.txt into the UNICODE encoded
file named myunicodefile.txt.
Note that myfile.txt should be ANSI for this to work correctly. |
| Script: |
1.
|
cmd /u /c type myfile.txt>myunicodefile.txt
|
|
| Description: |
Use parenthesis to group commands into a block. Command blocks are useful in combination with
e.g. IF or FOR commands.
An opening parenteses in a line will tell command processor that more lines will follow. |
| Script: |
Download: BatchCommandBlock.bat
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
|
@ECHO OFF
for /l %%a IN (4,-1,0) do (
echo.%%a: First command in block
echo. Second command in block
)
echo.
if exist "c:\windows" (
echo.The c:\windows directory exist.
set "IsWin=YES"
) ELSE (
set "IsWin=NO"
)
echo.Is this a windows pc? %IsWin%
|
|
| Script Output: |
 Script Output Script Output | 4: First command in block
Second command in block
3: First command in block
Second command in block
2: First command in block
Second command in block
1: First command in block
Second command in block
0: First command in block
Second command in block
The c:\windows directory exist.
Is this a windows pc? YES
| |
| Description: |
Use & to separate multiple commands within a single command line. |
| Script: |
1.
2.
|
cls&dir
for /l %%a IN (10,-1,0) do @echo.%%a:&echo.This is line number %%a
|
|
| Description: |
Command1 && SuccessCommand
Command1 || FailCommand
Command1 && SuccessCommand || FailCommand
The && operator can be used to execute a command only when the previews command succeeded.
The || operator can be used to execute a command only when the previews command failed.
Example 1
Show a message only when the string "ERROR" exist in the logfile.log file. The find command
succeeds when the string "ERROR" exist in logfile.log. The output of the find command is
redirected into the NUL devise since we don`t want to see any of its output in the output window.
Example 2
Show a message only when the string "ERROR" doesn`t exist in the logfile.log file. The find command
fails when the string "ERROR" doesn`t exist in logfile.log. The output of the find command is
redirected into the NUL devise since we don`t want to see any of its output in the output window.
Example 3
The Conditional Execution operators are useful with many DOS commands, i.e. the SET command.
Note
Be careful when combining the operators, i.e.:
Command1 && (CommandBlock2) || (CommandBlock3)
- If Command1 fails then CommandBlock2 will be skipped and CommandBlock3 will be executed.
- If Command1 succeeds then CommandBlock2 will be executed.
- If Command2 fails then CommandBlock3 will also be executed!!
To avoid this pitfall force CommandBlock2 to succeed, i.e. using a simple REM as last block command:
Command1 && (CommandBlock2 & REM) || (CommandBlock3)
or:
Command1 && (
CommandBlock2
REM force success
) || (
CommandBlock3
)
|
| Script: |
Download: BatchConditionalExecution.bat
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
|
@ECHO OFF
echo.
echo.1:
echo. ...finding 'ERROR' in logfile.log
find "ERROR" logfile.log>NUL && (
echo. yes, "ERROR" in logfile
)
echo.
echo.2:
echo. ...finding 'ERROR' in logfile.log
find "ERROR" logfile.log>NUL || (
echo. no "ERROR" in logfile
)
echo.
echo.3:
set "v=old_value"
set /p "v= ...enter a value or just hit ENTER: " && (
echo. The user entered a value, the variable v changed.
) || (
echo. The user just hit Enter, the variable v remains unchanged.
)
echo. v is now: %v%
|
|
| Script Output: |
 Script Output Script Output |
1:
...finding 'ERROR' in logfile.log
2:
...finding 'ERROR' in logfile.log
no "ERROR" in logfile
3:
...enter a value or just hit ENTER:
The user just hit Enter, the variable v remains unchanged.
v is now: old_value
| |
| Description: |
Running the FIND command with option /v and empty search string will find all lines
Running the FIND command with option /c will output the line count only.
The FOR command with option /f will parse the output, the line count in this case,
and the set command put the line number into the cnt variable. |
| Script: |
1.
2.
3.
4.
|
set file=textfile.txt
set /a cnt=0
for /f %%a in ('type "%file%"^|find "" /v /c') do set /a cnt=%%a
echo %file% has %cnt% lines
|
|
| Script Output: |
 Script Output Script Output | textfile.txt has 50 lines
| |
| Description: |
Knowing a certain character combination that never occurs in string1 can help solving the exercise.
Lets say @@@ never occurs in string1 then we can use it as prefix for string1 and reformulate the
question to: Does string1 alter if we delete any occurrence of @@@+string2 within string1.
If string1 alters then if string1 start string2 then string 1 will alter otherwise not. |
| Script: |
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
|
SETLOCAL ENABLEDELAYEDEXPANSION
set s=@@@%string1%
if "%s%"=="!s:@@@%string2%=!" (
echo.string1 doesn`t begin with string2
) ELSE (
echo.string1 begins with string2
)
|
|
| Description: |
The FSUTIL program can be used from the command line to query information about
the connected drives.
Return all currently connected drives:
fsutil fsinfo drives
Returns e.g.: Drives: C:\ D:\ E:\ F:\
Return the drive type for a given drive:
fsutil fsinfo drivetype D:\
Returns e.g.: D:\ - Fixed Drive
To get the drive type of all drives parse the output of fsutil fsinfo drives with
a FOR command and run fsutil fsinfo drivetype for each drive. However some
experimenting showed that funny things happen when parsing the result of fsutil fsinfo drives
using the FOR command, some line feeds seem to be missing. Piping the fsutil output through
the find command seems to resolve this problem. |
| Script: |
Download: BatchDriveType.bat
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
|
@ECHO OFF
set "drlist="
for /f "tokens=*" %%A in ('fsutil fsinfo drives^|find "\"') do (
set "dr=%%A"
call set "drlist=%%drlist%% %%dr:~-3%%"
)
for %%A in (%drlist%) do fsutil fsinfo drivetype %%A
|
|
| Script Output: |
 Script Output Script Output | C:\ - Fixed Drive
D:\ - Fixed Drive
E:\ - CD-ROM Drive
F:\ - Removable Drive
| |
| Description: |
To ouptut an empty line using the ECHO command simply append a dot to the command. Otherwise the
ECHO command will show the current echo state. In fact it appears to be safe to always use the dot.
A problem has been identified: "echo." stops working when there is a file named "echo" in the current
directory. Using "echo/" instead may be a better option. See
this forum post for details. |
| Script: |
1.
2.
3.
4.
|
echo
echo This line is followed by an empty line.
echo.
echo.Simply always use the dot when echoing text
|
|
| Script Output: |
 Script Output Script Output | ECHO is on.
This line is followed by an empty line.
Simply always use the dot when echoing text
| |
| Description: |
The command processor handles some characters in a special way and these characters won`t show up
in the output as expected when using i.e. the ECHO command. The exclamation mark is handled differently
if Delayed Expansion is enabled or disabled. |
| Script: |
Download: BatchEscape.bat
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
|
@ECHO OFF
SETLOCAL ENABLEEXTENSIONS
SETLOCAL DISABLEDELAYEDEXPANSION
echo.delayed expansion is DISABLED
echo.1. ^^! :exclamation mark
echo.2. !! :exclamation mark
echo.3. ! :exclamation mark
echo.4. %% :percent
echo.5. ^& :ampersand
echo.6. ^| :vertical line
echo.7. ^^ :caret
echo.
SETLOCAL ENABLEDELAYEDEXPANSION
echo.delayed expansion is ENABLED
echo.1. ^^! :exclamation mark
echo.2. !! :exclamation mark
echo.3. ! :exclamation mark
echo.4. %% :percent
echo.5. ^& :ampersand
echo.6. ^| :vertical line
echo.7. ^^ :caret
echo.
|
|
| Script Output: |
 Script Output Script Output | delayed expansion is DISABLED
1. ^! :exclamation mark
2. !! :exclamation mark
3. ! :exclamation mark
4. % :percent
5. & :ampersand
6. | :vertical line
7. ^ :caret
delayed expansion is ENABLED
1. ! :exclamation mark
2. exclamation mark
3. exclamation mark
4. % :percent
5. & :ampersand
6. | :vertical line
7. ^ :caret
| |
| Description: |
GOTO:EOF command will end a DOS batch application no matter whether subsequent code follow.
Adding a PAUSE command will allow the user to inspect screen outputs before the application
window disappears. Forcing an empty line via ECHO will nicely separate the "Press any key to
continue" message created by the PAUSE command from any previous output. |
| Script: |
1.
2.
|
::: -- End of application --
ECHO.&PAUSE&GOTO:EOF
|
|
| Description: |
Letting the PAUSE command show the "Press any key to continue" message on exit may cause some
confusion, since the application will finish and not continue. An ECHO command preceding the
PAUSE command can be used to show a customize message. The text output of the PAUSE command
can be omitted by piping its output into the NUL device. |
| Script: |
1.
2.
|
::: -- End of application --
ECHO.&ECHO.Press any key to end the application.&PAUSE>NUL&GOTO:EOF
|
|
| Description: |
As you develop DOS batch files you may find it annoying to have to hit a key when the application
finished just to close the window. You may want to have it close automatically but still being
able to briefly scan over the execution result shown in the window.
A way to create a delay in a DOS batch program is to ping the localhost or 127.0.0.1. Sending
2 pings (ping –n 2 ...) will cause a delay of very close to one second. Invoking multiple pings
as needed gives control about the delay time. Showing the remaining delay time in the window TITLE
will even let the user know what`s going on.
I.e. replace the pause statement added earlier with the following code lines and run the
application again. The menu will show a countdown of 5 seconds before closing the application.
Changing the number 5 to 10 would result in a 10 second countdown.
What it`s good for:
- Closing an application without user interaction
- Leave enough time to view execution results
- User can hit Pause on the keyboard to keep the window open
|
| Script: |
1.
2.
3.
|
::: -- End of application --
FOR /l %%a in (5,-1,1) do (TITLE %title% -- closing in %%as&ping -n 2 -w 1 127.0.0.1>NUL)
TITLE Press any key to close the application&ECHO.&GOTO:EOF
|
|
| Description: |
Use the `z` specifier of FOR variable references to get the size of a file. |
| Script: |
1.
2.
|
set "filename=myfile.txt"
for %%A in (%filename%) do echo.Size of "%%A" is %%~zA bytes
|
|
| Script Output: |
 Script Output Script Output | Size of "myfile.txt" is 57006 bytes
| |
| Description: |
At the beginning of a DOS batch file belongs the initialization of the command processor. This is
to ensure subsequent DOS batch script will be handled by the command interpreter as we intended to.
First let`s turn command-echoing off so that the output screen doesn`t get polluted with batch file
content itself during execution. Second, in order to enable the great features of the command
processor as required by most the other script code described here, the initialization code shall
turn on Extensions and Delayed Expansion. |
| Script: |
1.
2.
3.
4.
|
@echo off
REM.-- Prepare the Command Processor --
SETLOCAL ENABLEEXTENSIONS
SETLOCAL ENABLEDELAYEDEXPANSION
|
|
| Description: |
It`s known that opening the registry editor regedit.exe it will have the last registry key
remembered and opens right where the it left off the last time it was running. The last registry
key is being remembered in the registry itself using the LastKey value in
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Applets\Regedit.
To have regedit.exe open up at a specific location we just have to set the LastKey value properly
before invoking regedit.exe. This can be done with the REG command. |
| Script: |
1.
2.
3.
4.
|
rem open regedit.exe at HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft
set "showkey=HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft"
REG ADD "HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Applets\Regedit" /v "LastKey" /d "%showkey%" /f
start /b regedit
|
|
| Description: |
Force a batch to run as different user via RunAs command. This snippet checks the USERNAME
environment variable. If it`s not `Administrator` then it automatically restart the batch with
Administrator credentials using the RunAs command. Administrator password is required. |
| Script: |
Download: DosRunAsAdmin.bat
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
|
@echo off
echo.Current User is '%USERNAME%'
rem -- Let's make sure this batch runs as Administrator --
set "RunAsUser=Administrator"
if "%USERNAME%" NEQ "%RunAsUser%" (
RUNAS /user:%RunAsUser% "cmd /c %~f0"||PAUSE
GOTO:EOF
)
rem -- your code goes below here --
echo.Hello World
ECHO.&PAUSE&GOTO:EOF
|
|
| Script Output: |
 Script Output Script Output | Current User is 'DosItHelp'
Enter the password for Administrator:
Attempting to start cmd /c C:\dostips\DosRunAsAdmin.bat as user "DOSTIPS_PC\Administrator" ...
---- RunAs now opens a new window ----
Current User is 'Administrator'
Hello World
Press any key to continue . . .
| |
| Description: |
Use ^ as the very last character in a line if you with to continue the command in the next line. |
| Script: |
1.
2.
3.
4.
|
echo.1. This all goes ^
in line one
echo.2. This all goes ^
in line two
|
|
| Script Output: |
 Script Output Script Output | 1. This all goes in line one
2. This all goes in line two
| |
| Description: |
An easy way to convert an UNICODE encoded file to ANSI is by running a TYPE
command in a new instance of CMD.exe with /A option and piping the output into a new file.
The following script converts a text file named myfile.txt into the ANSI encoded
file named myansifile.txt.
Note myfile.txt can be UNICODE or ANSI the result will always be an ANSI encoded file. |
| Script: |
1.
|
cmd /a /c type myfile.txt>myansifile.txt
|
|
| Description: |
A string unique to the local host can be created out of the %date% and %time% system
environment variables.
For convenience the unique string created here will be a number in the format YYYYMMDDHHMMSSff
whereas ff are the 1/100th fractions of a second. As long nobody modifies the system time and the
command is not being called twice within a 1/100th of a second, each created UNIQUE string
will be unique and in a sorting order.
The example described here assumes that the %date% variable uses the format
day MM/DD/YYYY and the %time% variable uses the format HH:MM:SS.ff.
As the %time% variable may return only one digit for the hour before 10.00 AM and put
a spacer to fill the missing 10th digit we will substitute the space characters in %time% with 0
by using %time: =0%. |
| Script: |
1.
2.
3.
4.
|
for /f "tokens=2-8 delims=/:. " %%A in ("%date%:%time: =0%") do set "UNIQUE=%%C%%A%%B%%D%%E%%F%%G"
echo.%UNIQUE%
echo.%date% %time%
echo.%date% %time: =0%
|
|
| Script Output: |
 Script Output Script Output | 2006010501060696
Thu 01/05/2006 1:06:06.96
Thu 01/05/2006 01:06:06.96
| |
| Description: |
Having a version history within you DOS batch file is good practice in order to keep track of
when changed what. Have the following code block close to the beginning of each batch file to
present a nicely formatted version history. The version history can be updated by copying the
last entry and modifying Date, Author, and Description appropriately. |
| Script: |
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
|
::: -- Version History –-
::: XX.XXX YYYYMMDD Author Description
SET "version=01.000-beta" &:20051201 p.h. initial version, providing the framework
SET "version=01.000" &:20051202 p.h. framework ready
SET "version=01.001" &:20051203 p.h. added cool new features
::: !! For a new version entry, copy the last entry down and modify Date, Author and Description
|
|
| Description: |
The background and foreground color of a window can be changed using the COLOR command followed
by two hexadecimal digits:
1st - background
2nd - foreground
The change will appear instantly for the whole window.
The color codes are:
0 = Black 8 = Gray
1 = Blue 9 = Light Blue
2 = Green A = Light Green
3 = Aqua B = Light Aqua
4 = Red C = Light Red
5 = Purple D = Light Purple
6 = Yellow E = Light Yellow
7 = White F = Bright White
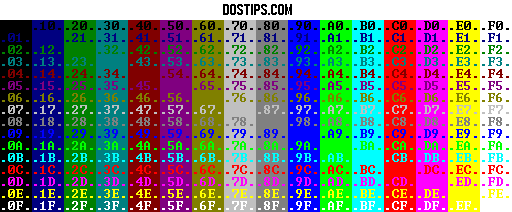 |
| Script: |
1.
2.
|
::: -- Set the window color --
COLOR 1A
|
|
| Description: |
To control the size of a window use the MODE command. The example shows how to size a window 90
characters horizontal and 10 lines vertical. |
| Script: |
1.
2.
|
::: -- Set the window size --
MODE CON: COLS=90 LINES=10
|
|
| Description: |
Application name and version of you application seem to make just the right title for the
application window. Let`s store the title into a variable that way it can be reused later
in the batch script in case we use the window title temporary to display something else.
The TITLE command will set the window title. |
| Script: |
1.
2.
3.
|
::: -- Set the window title --
SET "title=%~nx0 - version %version%"
TITLE %title%
|
|
| Description: |
Use the `z` specifier of FOR variable references to get the size of a file. Then show or delete
the file if the size is zero. |
| Script: |
1.
2.
|
set "filemask=myfile*.txt"
for %%A in (%filemask%) do if %%~zA==0 echo."%%A" is empty
|
|
| Script Output: |
 Script Output Script Output | "myfile2.txt" is empty
"myfile7.txt" is empty
"myfile8.txt" is empty
| |
